- Processor: NVIDIA Tegra 4 Quad Core Mobile Processor with 2GB RAM
- Display: 5 inch 1280x720 Multi-Touch Retinal Quality Display
- Audio: Integrated Stereo Speakers with Built-in Microphone
- Storage: 16GB Flash Memory
- Wireless: 802.11n 2x2 MIMO Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 3.0, GPS
NVIDIA SHIELD 16GB, now $249.99 & FREE Shipping
Detect Gesture by implementing GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener
This example show how to detect user gesture by implementing GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener. It have the same result as last exercise of "GestureDetector".
GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener provides an implementation for all of the on<TouchEvent> methods by returning false for all of them. Thus we can override only the methods we care about. In our application, we have to detect onFling() only. So we can extend GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener instead of implementing the GestureDetector.OnGestureListener interface.
MainActivity.java
Keep using the layout and animation XML files in the exercise of "Bi-direction sliding ViewFlipper".
 Download the files.
Download the files.
GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener provides an implementation for all of the on<TouchEvent> methods by returning false for all of them. Thus we can override only the methods we care about. In our application, we have to detect onFling() only. So we can extend GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener instead of implementing the GestureDetector.OnGestureListener interface.
MainActivity.java
package com.example.androidviewflipper;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v4.view.GestureDetectorCompat;
import android.view.GestureDetector;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.widget.ViewFlipper;
public class MainActivity extends Activity{
private GestureDetectorCompat mDetector;
Button buttonPrev, buttonNext;
ViewFlipper viewFlipper;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
Animation slide_in_right, slide_out_left;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mDetector = new GestureDetectorCompat(this, new MyGestureListener());
buttonPrev = (Button) findViewById(R.id.prev);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
viewFlipper = (ViewFlipper) findViewById(R.id.viewflipper);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_out_right);
slide_in_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_in_right);
slide_out_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_out_left);
buttonPrev.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_right);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_left);
viewFlipper.showPrevious();
}
});
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
viewFlipper.showNext();
}
});
;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
this.mDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
class MyGestureListener extends GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener {
@Override
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
float sensitvity = 50;
if((e1.getX() - e2.getX()) > sensitvity){
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_right);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_left);
viewFlipper.showPrevious();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"Previous", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else if((e2.getX() - e1.getX()) > sensitvity){
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
viewFlipper.showNext();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"Next", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
return true;
}
}
}
Keep using the layout and animation XML files in the exercise of "Bi-direction sliding ViewFlipper".
Using GestureDetector to detect user swipe, onFling()
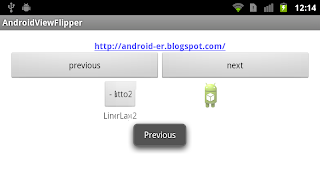
Previous exercise demonstrate "Bi-direction sliding ViewFlipper" controlled by buttons. This exercise show how to implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener to detect user swipe to update ViewFlipper.
Keep using the layout and animation XML files in last exercise.
 Download the files.
Download the files.
Next:
- Detect Gesture by implementing GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener
package com.example.androidviewflipper;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v4.view.GestureDetectorCompat;
import android.view.GestureDetector;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.widget.ViewFlipper;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements
GestureDetector.OnGestureListener {
private GestureDetectorCompat mDetector;
Button buttonPrev, buttonNext;
ViewFlipper viewFlipper;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
Animation slide_in_right, slide_out_left;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mDetector = new GestureDetectorCompat(this,this);
buttonPrev = (Button) findViewById(R.id.prev);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
viewFlipper = (ViewFlipper) findViewById(R.id.viewflipper);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_out_right);
slide_in_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_in_right);
slide_out_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_out_left);
//viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
//viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
buttonPrev.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_right);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_left);
viewFlipper.showPrevious();
}
});
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
viewFlipper.showNext();
}
});
;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
this.mDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
float sensitvity = 50;
if((e1.getX() - e2.getX()) > sensitvity){
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_right);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_left);
viewFlipper.showPrevious();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"Previous", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else if((e2.getX() - e1.getX()) > sensitvity){
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
viewFlipper.showNext();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"Next", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX,
float distanceY) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
@Override
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}
Keep using the layout and animation XML files in last exercise.
Next:
- Detect Gesture by implementing GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener
Download The Windows Getting Started Guide
This guide will point you to the right developer tools, tutorials, and resources. Jump in. The next generation is what you make it.
Download here.
and more resources on Microsoft Student web site.
Download here.
and more resources on Microsoft Student web site.
Java Programming for Android Developers For Dummies
Get started creating Android apps with Java in no time!
The demand for Android apps is not slowing down but many mobile developers who want to create Android apps lack the necessary Java background. This beginner guide gets you up and running with using Java to create Android apps with no prior knowledge or experienced necessary!
- Shows you the basic Java development concepts and techniques that are necessary to develop Android apps
- Explores what goes into creating an Android app to give you a better understanding of the various elements
- Addresses how to deal with standard programming challenges and debugging
Beginning Android Programming with Java For Dummies puts you well on your way toward creating Android apps quickly with Java.
Publication Date: November 4, 2013 | ISBN-10: 1118504380 | ISBN-13: 978-1118504383 | Edition: 1
Android Programming: Pushing the Limits
Unleash the power of the Android OS and build the kinds of brilliant, innovative apps users love to use
If you already know your way around the Android OS and can build a simple Android app in under an hour, this book is for you. If you’re itching to see just how far you can push it and discover what Android is really capable of, it’s for you. And if you’re ready to learn how to build advanced, intuitive, innovative apps that are a blast to use, this book is definitely for you.
From custom views and advanced multi-touch gestures, to integrating online web services and exploiting the latest geofencing and activity recognition features, ace Android developer, Erik Hellman, delivers expert tips, tricks and little-known techniques for pushing the Android envelope so you can:
- Optimize your components for the smoothest user experience possible
- Create your own custom Views
- Push the boundaries of the Android SDK
- Master Android Studio and Gradle
- Make optimal use of the Android audio, video and graphics APIs
- Program in Text-To-Speech and Speech Recognition
- Make the most of the new Android maps and location API
- Use Android connectivity technologies to communicate with remote devices
- Perform background processing
- Use Android cryptography APIs
- Find and safely use hidden Android APIs
- Cloud-enable your applications with Google Play Services
- Distribute and sell your applications on Google Play Store
Learn how to unleash the power of Android and transform your apps from good to great in Android Programming: Pushing the Limits.
Publication Date: November 4, 2013 | ISBN-10: 1118717376 | ISBN-13: 978-1118717370 | Edition: 1
How to build Open JavaFX for Android
Here (https://blogs.oracle.com/jfxprg/entry/how_to_build_open_javafx) is a short recipe for baking JavaFX for Android dalvik. Just a few ingredients needed but each one requires special care.
Bi-direction sliding ViewFlipper
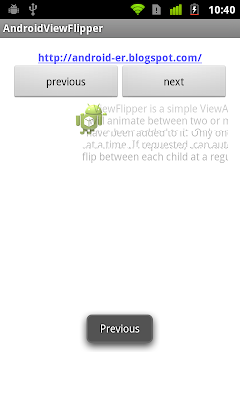
Last exercise show a Example of ViewFlipper. It always slide from left to right, no matter you click previous or next button. In this exercise, we will implement bi-direction sliding. Slide to right if you click next button, slide left if you click previous button. This technique can also be applied on ViewAnimator, TextSwitcher, ImageSwitcher and ViewSwitcher.
Create /res/anim/ folder, and create the following XMLs to define the animation.
slide_in_left.xml:
slide_in_right.xml:
slide_out_left.xml:
slide_out_right.xml:
Modify layout file, all child View of <ViewFlipper> have android:layout_width="match_parent".
Main code;
Next: Using GestureDetector to detect user swipe, onFling()
Create /res/anim/ folder, and create the following XMLs to define the animation.
slide_in_left.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate android:fromXDelta="-50%p" android:toXDelta="0"
android:duration="1000"/>
<alpha android:fromAlpha="0.0" android:toAlpha="1.0"
android:duration="1000" />
</set>
slide_in_right.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate android:fromXDelta="50%p" android:toXDelta="0"
android:duration="1000"/>
<alpha android:fromAlpha="0.0" android:toAlpha="1.0"
android:duration="1000" />
</set>
slide_out_left.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate android:fromXDelta="0" android:toXDelta="-50%p"
android:duration="1000"/>
<alpha android:fromAlpha="1.0" android:toAlpha="0.0"
android:duration="1000" />
</set>
slide_out_right.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate android:fromXDelta="0" android:toXDelta="50%p"
android:duration="1000"/>
<alpha android:fromAlpha="1.0" android:toAlpha="0.0"
android:duration="1000" />
</set>
Modify layout file, all child View of <ViewFlipper> have android:layout_width="match_parent".
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:autoLink="web"
android:text="http://android-er.blogspot.com/"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/prev"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="previous" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="next" />
</LinearLayout>
<ViewFlipper
android:id="@+id/viewflipper"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Button 2 -" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="LinearLayout 2" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Enter something" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="LinearLayout 3" />
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="ViewFlipper is a simple ViewAnimator that
will animate between two or more views that
have been added to it. Only one child is shown
at a time. If requested, can automatically
flip between each child at a regular interval." />
</ViewFlipper>
</LinearLayout>
Main code;
package com.example.androidviewflipper;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ViewFlipper;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button buttonPrev, buttonNext;
ViewFlipper viewFlipper;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
Animation slide_in_right, slide_out_left;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonPrev = (Button) findViewById(R.id.prev);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
viewFlipper = (ViewFlipper) findViewById(R.id.viewflipper);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_out_right);
slide_in_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_in_right);
slide_out_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.slide_out_left);
//viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
//viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
buttonPrev.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_right);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_left);
viewFlipper.showPrevious();
}
});
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
viewFlipper.showNext();
}
});
;
}
}
Next: Using GestureDetector to detect user swipe, onFling()
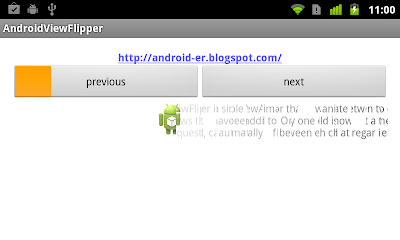
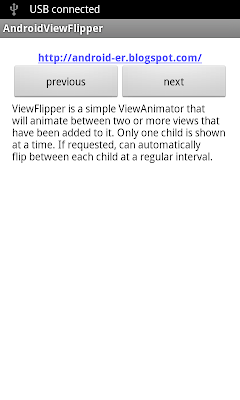
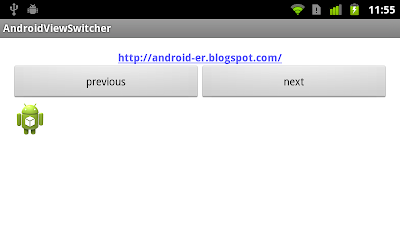
Example of ViewFlipper
android.widget.ViewFlipper is a simple ViewAnimator that will animate between two or more views that have been added to it. Only one child is shown at a time. If requested, can automatically flip between each child at a regular interval.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:autoLink="web"
android:text="http://android-er.blogspot.com/"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/prev"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="previous" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="next" />
</LinearLayout>
<ViewFlipper
android:id="@+id/viewflipper"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Button 2 -" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="LinearLayout 2" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Enter something" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="LinearLayout 3" />
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="ViewFlipper is a simple ViewAnimator that
will animate between two or more views that
have been added to it. Only one child is shown
at a time. If requested, can automatically
flip between each child at a regular interval." />
</ViewFlipper>
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.androidviewflipper;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ViewFlipper;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button buttonPrev, buttonNext;
ViewFlipper viewFlipper;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonPrev = (Button) findViewById(R.id.prev);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
viewFlipper = (ViewFlipper) findViewById(R.id.viewflipper);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_out_right);
viewFlipper.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewFlipper.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
buttonPrev.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.showPrevious();
}
});
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewFlipper.showNext();
}
});
;
}
}
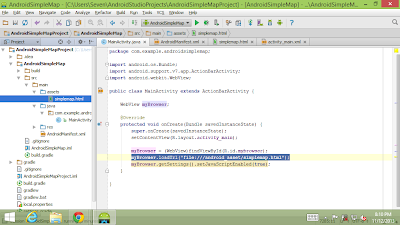
assets folder in Android Studio
Android Studio is a new Android development environment based on IntelliJ IDEA, Gradle-based build support. It have different project structure.
In Eclipse, assets is in /assets folder under your project. In Android Studio, it is in /src/main/assets. In both Eclipse and Android Studio, /assets have the same level of /res folder.
Compare with the exercise of "Embed html using Google Maps JavaScript API v3 in Android App", where /assets/simplemap.html is a asset file of HTML. In Android Studio, it in /src/main/assets/simplemap.html. In both case, it can be accessed with "file:///android_asset/simplemap.html".
reference: Gradle Plugin User Guide > Project Structure
In Eclipse, assets is in /assets folder under your project. In Android Studio, it is in /src/main/assets. In both Eclipse and Android Studio, /assets have the same level of /res folder.
Compare with the exercise of "Embed html using Google Maps JavaScript API v3 in Android App", where /assets/simplemap.html is a asset file of HTML. In Android Studio, it in /src/main/assets/simplemap.html. In both case, it can be accessed with "file:///android_asset/simplemap.html".
reference: Gradle Plugin User Guide > Project Structure
Example of ViewSwitcher
android.widget.ViewSwitcher is a sub-class of ViewAnimator, switches between two views, and has a factory from which these views are created. You can either use the factory to create the views, or add them yourself.
A ViewSwitcher can only have two child views, of which only one is shown at a time. If you have more than two child views in ViewSwitch, java.lang.IllegalStateException of "Can't add more than 2 views to a ViewSwitcher" will happen.
- Compare with ViewAnimator
A ViewSwitcher can only have two child views, of which only one is shown at a time. If you have more than two child views in ViewSwitch, java.lang.IllegalStateException of "Can't add more than 2 views to a ViewSwitcher" will happen.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:autoLink="web"
android:text="http://android-er.blogspot.com/"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/prev"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="previous" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="next" />
</LinearLayout>
<ViewSwitcher
android:id="@+id/viewswitcher"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Button 2 -" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="LinearLayout 2" />
</LinearLayout>
</ViewSwitcher>
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.androidviewswitcher;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ViewSwitcher;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button buttonPrev, buttonNext;
ViewSwitcher viewSwitcher;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonPrev = (Button) findViewById(R.id.prev);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
viewSwitcher = (ViewSwitcher) findViewById(R.id.viewswitcher);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_out_right);
viewSwitcher.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewSwitcher.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
buttonPrev.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewSwitcher.showPrevious();
}
});
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewSwitcher.showNext();
}
});
;
}
}
- Compare with ViewAnimator
Good official lessons teach Caching Bitmaps and Managing Bitmap Memory
When your app have to load a number of bitmap, memory allocation will get complicated. Here is official lessons from developer.android.com.
- Caching Bitmaps teach you using a memory and disk bitmap cache to improve the responsiveness and fluidity of your UI when loading multiple bitmaps.
- Managing Bitmap Memory teach specific things you can do to facilitate garbage collection and bitmap reuse.
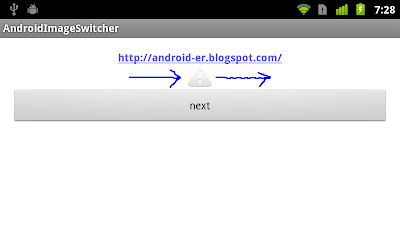
Android example: ImageSwitcher
A simple example to implement ImageSwitcher.
package com.example.androidimageswitcher;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageSwitcher;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button buttonNext;
ImageSwitcher imageSwitcher;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
int imageResources[] = {
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_alert,
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_dialer,
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_email,
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_info,
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_map };
int curIndex;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
imageSwitcher = (ImageSwitcher) findViewById(R.id.imageswitcher);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_out_right);
imageSwitcher.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
imageSwitcher.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
imageSwitcher.setFactory(new ViewFactory() {
@Override
public View makeView() {
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(MainActivity.this);
imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_CENTER);
LayoutParams params = new ImageSwitcher.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
imageView.setLayoutParams(params);
return imageView;
}
});
curIndex = 0;
imageSwitcher.setImageResource(imageResources[curIndex]);
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
if (curIndex == imageResources.length - 1) {
curIndex = 0;
imageSwitcher.setImageResource(imageResources[curIndex]);
} else {
imageSwitcher.setImageResource(imageResources[++curIndex]);
}
}
});
}
}
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:autoLink="web"
android:text="http://android-er.blogspot.com/"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<ImageSwitcher
android:id="@+id/imageswitcher"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="next" />
</LinearLayout>
ListFragment with multiple choice
It is a example to implement ListFragment with multiple choice.
Base on my old exercise of "ListFragment".
Modify MyListFragment1.java, create ListAdapter with android.R.layout.simple_list_item_multiple_choice. Also modify onListItemClick() to display the clicked item and selected items.
Modify listfragment1.xml to add android:choiceMode="multipleChoice" in <ListView>.
 Download the files.
Download the files.
Base on my old exercise of "ListFragment".
Modify MyListFragment1.java, create ListAdapter with android.R.layout.simple_list_item_multiple_choice. Also modify onListItemClick() to display the clicked item and selected items.
package com.exercise.AndroidListFragment;
import android.app.ListFragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.SparseBooleanArray;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MyListFragment1 extends ListFragment {
String[] month ={
"January",
"February",
"March",
"April",
"May",
"June",
"July",
"August",
"September",
"October",
"November",
"December"
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ListAdapter myListAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(
getActivity(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_multiple_choice,
month);
setListAdapter(myListAdapter);
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.listfragment1, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
String prompt =
"clicked item: " + getListView().getItemAtPosition(position).toString() + "\n\n";
prompt += "selected items: \n";
int count = getListView().getCount();
SparseBooleanArray sparseBooleanArray = getListView().getCheckedItemPositions();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){
if (sparseBooleanArray.get(i)) {
prompt += getListView().getItemAtPosition(i).toString() + "\n";
}
}
Toast.makeText(
getActivity(),
prompt,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
Modify listfragment1.xml to add android:choiceMode="multipleChoice" in <ListView>.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingLeft="8dp"
android:paddingRight="8dp" >
<ListView
android:id="@id/android:list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:choiceMode="multipleChoice"
android:drawSelectorOnTop="false" />
<TextView
android:id="@id/android:empty"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="No data" />
</LinearLayout>
Example to implement Android TextSwitcher
android.widget.TextSwitcher is a specialized ViewSwitcher that contains only children of type TextView. A TextSwitcher is useful to animate a label on screen. Whenever setText(CharSequence) is called, TextSwitcher animates the current text out and animates the new text in.
Example code to implement TextSwitcher.
Example code to implement TextSwitcher.
package com.example.androidtextswitcher;
import com.example.androidviewanimator.R;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Typeface;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextSwitcher;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button buttonNext;
TextSwitcher textSwitcher;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
String[] TextToSwitched = { "Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday",
"Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday" };
int curIndex;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
textSwitcher = (TextSwitcher) findViewById(R.id.textswitcher);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.slide_out_right);
textSwitcher.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
textSwitcher.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
textSwitcher.setFactory(new ViewFactory(){
@Override
public View makeView() {
TextView textView = new TextView(MainActivity.this);
textView.setTextSize(30);
textView.setTextColor(Color.RED);
textView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL);
textView.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD);
textView.setShadowLayer(10, 10, 10, Color.BLACK);
return textView;
}});
curIndex = 0;
textSwitcher.setText(TextToSwitched[curIndex]);
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
if(curIndex == TextToSwitched.length-1){
curIndex = 0;
textSwitcher.setText(TextToSwitched[curIndex]);
}else{
textSwitcher.setText(TextToSwitched[++curIndex]);
}
}
});
}
}
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:autoLink="web"
android:text="http://android-er.blogspot.com/"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<TextSwitcher
android:id="@+id/textswitcher"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="next" />
</LinearLayout>
Example of ViewAnimator
android.widget.ViewAnimator is a subclass of FrameLayout container that will perform animations when switching between its views.
more related example:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:autoLink="web"
android:text="http://android-er.blogspot.com/"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/prev"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="previous" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="next" />
</LinearLayout>
<ViewAnimator
android:id="@+id/viewanimator"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView 1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Button 4 -" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="LinearLayout 4" />
</LinearLayout>
</ViewAnimator>
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.androidviewanimator;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ViewAnimator;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button buttonPrev, buttonNext;
ViewAnimator viewAnimator;
Animation slide_in_left, slide_out_right;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonPrev = (Button)findViewById(R.id.prev);
buttonNext = (Button)findViewById(R.id.next);
viewAnimator = (ViewAnimator)findViewById(R.id.viewanimator);
slide_in_left = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, android.R.anim.slide_in_left);
slide_out_right = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, android.R.anim.slide_out_right);
viewAnimator.setInAnimation(slide_in_left);
viewAnimator.setOutAnimation(slide_out_right);
buttonPrev.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewAnimator.showPrevious();
}});
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
viewAnimator.showNext();
}});
}
}
more related example:
- ViewSwitcher
- ImageSwitcher
- TextSwitcher
- ViewFlipper
- Bi-direction sliding
- Using GestureDetector to detect user swipe, onFling()
- Detect Gesture by implementing GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener
الاشتراك في:
الرسائل (Atom)